SHEET METAL WORKING
Sheet metal is simply metal formed into thin and flat pieces. It is one of the fundamental forms used in metalworking, and can be cut and bent into a variety of different shapes. Countless everyday objects are constructed of the material. Thicknesses can vary significantly, although extremely thin thicknesses are considered foil or leaf, and pieces thicker than 6 mm (0.25 in) are considered plate.
Sheet metal processing
The raw material for sheet metal manufacturing processes is the output of the rolling process. Typically, sheets of metal are sold as flat, rectangular sheets of standard size. If the sheets are thin and very long, they may be in the form of rolls. Therefore the first step in any sheet metal process is to cut the correct shape and sized ‘blank’ from larger sheet.
Sheet metal forming processes
Sheet metal processes can be broken down into two major classifications and one minor classification
Shearing processes
processes which apply shearing forces to cut, fracture, or separate the material.
Forming processes
processes which cause the metal to undergo
desired shape changes without failure, excessive thinning, or cracking. This includes bending and stretching.
Finishing processes
processes which are used to improve the final surface characteristics.
Shearing Process
1. Punching: shearing process using a die and punch where the interior portion of the sheared sheet is to be discarded.
2. Blanking: shearing process using a die and punch where the exterior portion of the shearing operation is to be discarded.
3. Perforating: punching a number of holes in a sheet.
4. Parting: shearing the sheet into two or more pieces.
5. Notching: removing pieces from the edges.
6. Lancing: leaving a tab without removing any material.
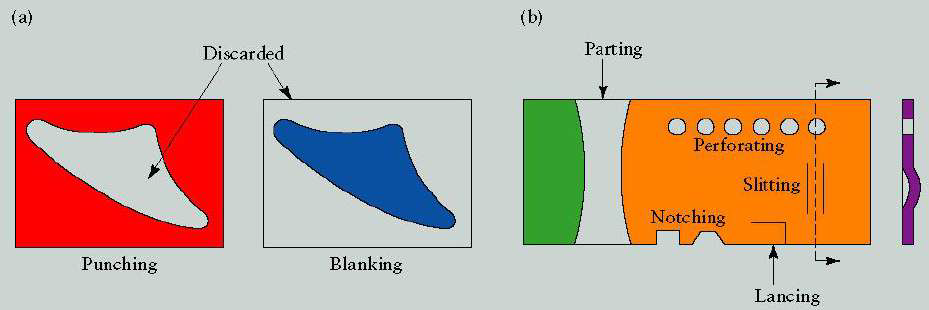 |
| Shearing Operations: Punching, Blanking and Perforating |
Forming Processes
Bending: forming process causes the sheet metal to undergo the desired shape change by bending without failure. Ref fig.2 & 2a
Stretching: forming process causes the sheet metal to undergo the desired shape change by stretching without failure. Ref fig.3
Drawing: forming process causes the sheet metal to undergo the desired shape change by drawing without failure.
Roll forming: Roll forming is a process by which a metal strip is progressively bent as it passes through a series of forming rolls.
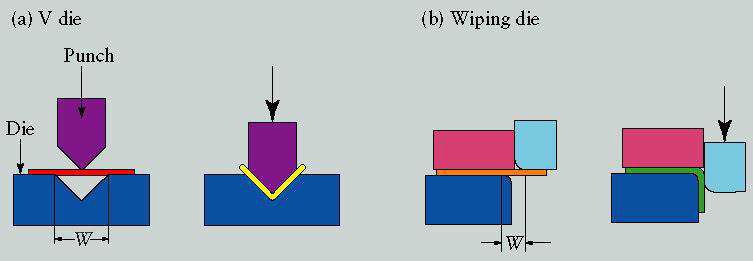 |
| Common Die-Bending Operations |
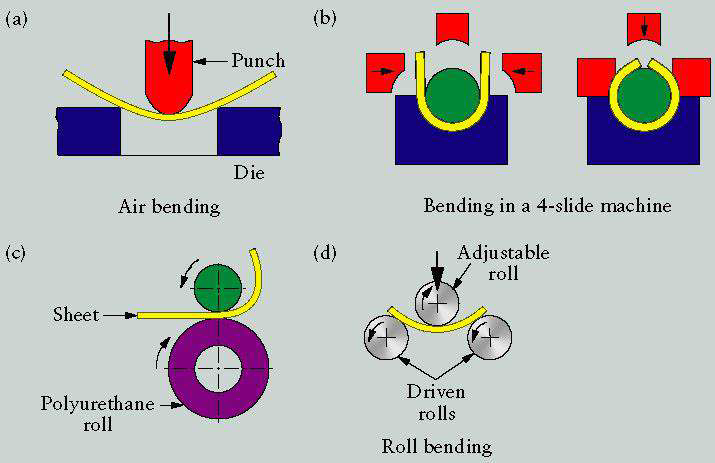 |
| Various Bending Operations |
 |
| Schematic illustration of a stretch-forming process |
Merits
High strength
Good dimensional accuracy and surface finish
Relatively low cost
Demerits
Wrinkling and tearing are typical limits to drawing operations
Different techniques can be used to overcome these limitations
- Draw beads
- Vertical projections and matching grooves in the die and
- blank holder
Trimming may be used to reach final dimensions
Applications
Roofings
Ductings
Vehicles body buildings like 3 wheelers, 4 wheelers, ships, aircrafts etc.
Furnitures, House hold articles and Railway equipment